Ozymandias is a proof-of-concept biodiversity knowledge graph by Rod Page @rdmpage.
 Page RDM. 2019. Ozymandias: a biodiversity knowledge graph. PeerJ 7:e6739 https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.6739
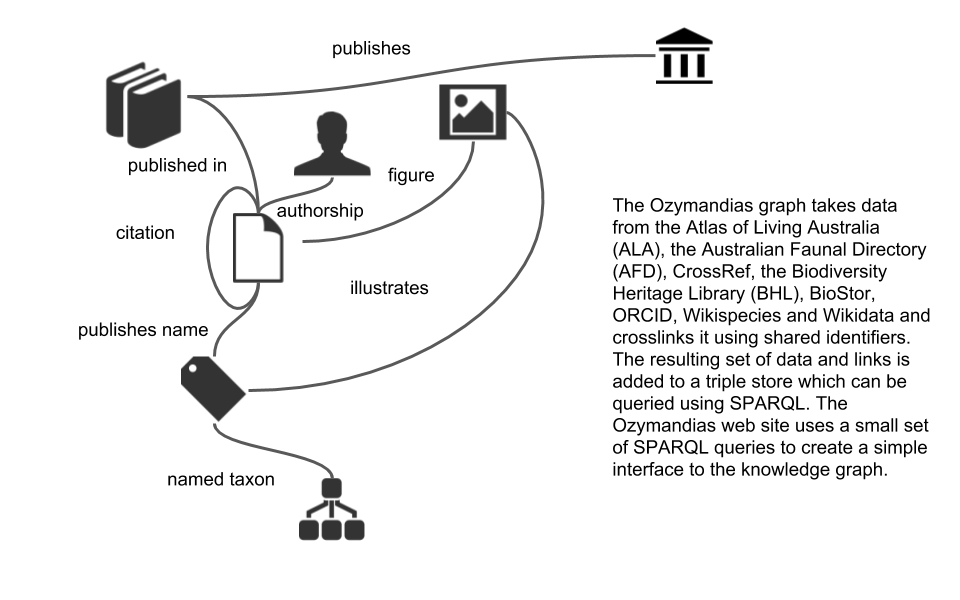
Page RDM. 2019. Ozymandias: a biodiversity knowledge graph. PeerJ 7:e6739 https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.6739The core of this knowledge graph is a classification of animals from the Atlas of Living Australia (ALA) combined with data on taxonomic names and publications from the Australian Faunal Directory (AFD). This has been enhanced by adding lots of digital identifiers (such as DOIs) to the publications and, where possible, full text either as PDFs or as page scans from the Biodiversity Heritage Library (BHL) (provided via BioStor). Identifiers enable us to further grow the knowledge graph, for example by adding "cites" and "cited by" links between publications (data from CrossRef), and displaying figures from the Biodiversity Literature Repository (BLR).
Technical details
TL;DR the knowledge graph is implemented as a triple store where the data has been represented using a small number of vocabularies (mostly schema.org with some terms borrowed from TAXREF-LD and the TDWG LSID vocabularies). All results displayed in the first two panels are the result of SPARQL queries, the content in the rightmost panel comes from calls to external APIs. Search is implemented using Elasticsearch. If you are feeling brave you can query the knowledge graph directly in SPARQL.



